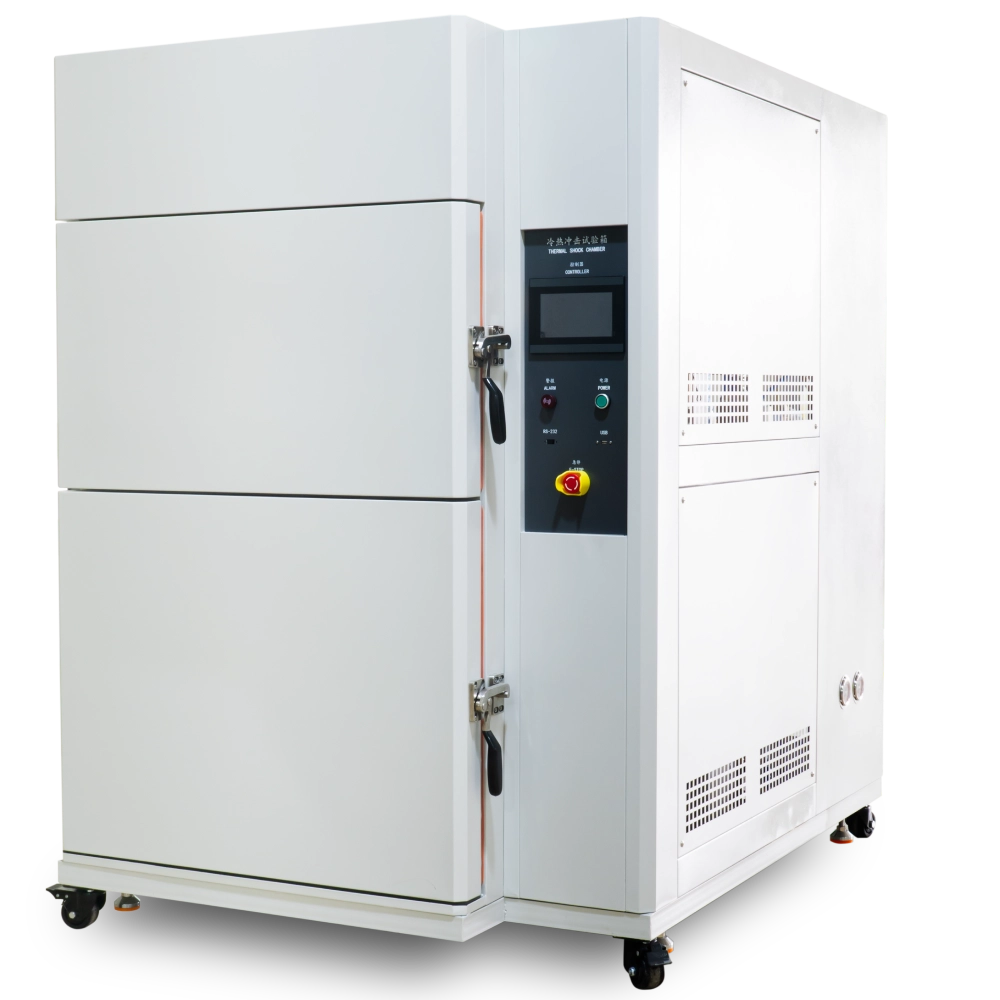
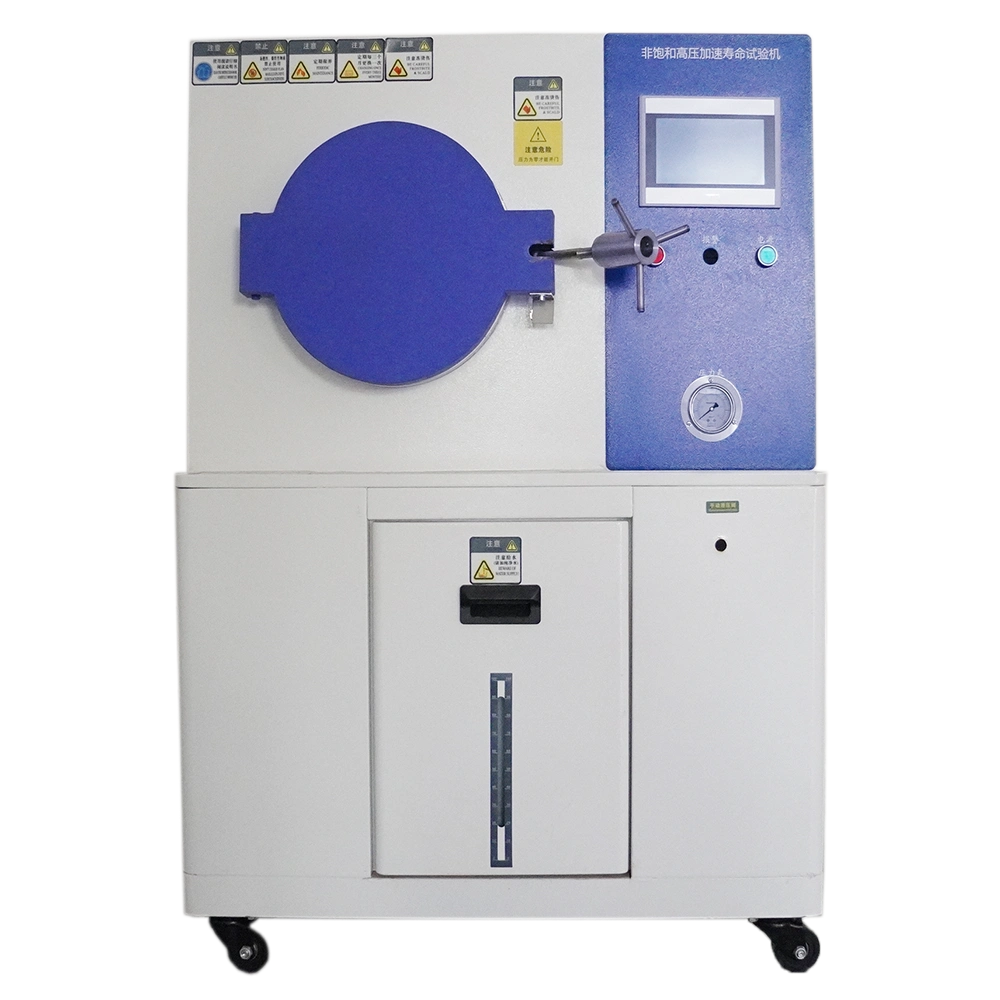
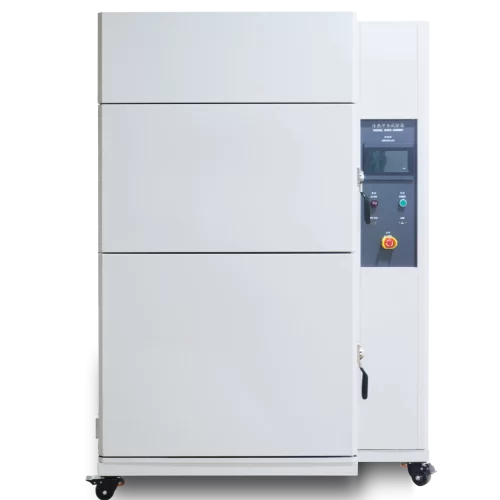
The impact tester tests how temperature affects various materials and components. It functions for electronic and electrical parts, metals, chemicals, and more. It is an ideal test tool for studying physical changes. This thermal shock chamber is perfect for testing physical changes in electrical and electronic components. It is also ideal for testing metals and chemical materials. Additionally, it is suitable for testing automation parts and communication components. Moreover, the defense and aerospace industries use it. Furthermore, users use it to test BGAs, PCB substrates, and electronic chip ICs. Also, people use it to test semiconductor ceramics and polymer materials.
Technical characteristics of our temperature impact tester:
- USB disk recording function, no logger required.
- Refrigerant servo valve flow algorithm control. Power saving 30%.
- High temperature and high humidity test to prevent condensation, dripping technology industry-leading
- In cold working conditions, the heater does not work. It adjusts the refrigerant flow and direction using PWM technology. It controls the refrigeration unit. It controls three pipelines: refrigeration, cold bypass, and hot bypass. It does this to keep the studio at a constant temperature. This method can reduce energy consumption by 40% under low temperature conditions.
- Temperature synchronization slope control (IEC68-2-56,68-2-30), no dripping, no condensation and condensation
- Refrigeration has advantages. Traditional equipment uses a start-stop control mode for low temperatures. This mode has a problem. Fluctuations in temperature greatly affect the compressor’s life. The technology has been eliminated.
Control mode of temperature shock test chamber:
Thermal shock machine uses low and high temperature storage tanks and thermal energy storage tanks. To achieve a rapid temperature shock effect, open the DAMPER. Hot and cold energy is then transferred into the test tank. It has a balance temperature control system (BTC). It also has a designed air supply circulation system. A dynamic P.I.D. method controls the SSR. This ensures that the system’s heating matches the amount of heat loss. As a result, users can use the system for a long time and it remains stable.
thermal shock chamber Technical parameters:
Product name: Two-box type cold and heat shock test chamber
Brand and product model: JS-150TC-40
Test method:
Pneumatic air door switch double temperature zone, water-cooled type
Specimen limit
This temperature shock chamber prohibits:
- The test and storage of flammable, explosive, volatile substances specimens
- The test and storage of corrosive material specimens
- Biological specimen testing or storage
- Strong electromagnetic emission source test and storage of specimens
- Test and storage of radioactive material specimens
- Testing and storage of highly toxic substances specimens
- The test process may produce toxic substances in the specimen. The storage process may also produce toxic substances in the specimen.
Volume and Size
| Machine type | 50 | 100 | 150 | 50 | 80 | 150 | 50 | 80 | 150 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-cooled | Air-cooled | Water-cooled | Air-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | ||||||||
| High temperature setting range | +60℃~+180℃ | +60℃~+180℃ | +60℃~+180℃ | |||||||||||||
| High and low impact temperatures | +150℃ | |||||||||||||||
| Low Temperature Setting Range | -70℃~-10℃ | -65℃~-10℃ | -75℃~-10℃ | |||||||||||||
| 5.5 Low temperature shock temperature | -40℃ | -55℃ | -65℃ | |||||||||||||
| High and low temperature impact range | -40℃~+150℃ | -55℃~+150℃ | -65℃~+150℃ | |||||||||||||
| Preheating warming time | +20~+180℃,≤60min | |||||||||||||||
| Pre-cooling cooling time | +20~-70℃,≤80min | +20~-65℃,≤80min | +20~-75℃,≤90min | |||||||||||||
| Temperature transition time | ≤10 seconds | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature rise and fall overshoot | ≤±3℃ | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature stabilization time | ≤3MIN | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature recovery performance | 30min | 30min | 30min | |||||||||||||
| Load (Plastic IC) | 10KG | 10KG | 2.5KG 5KG 7.5KG | |||||||||||||
| Compressor Selection | Blog / Copeland Emerson / Terracon France | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature Fluctuation | ±0.5℃ | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature deviation | ≦±2℃ | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature uniformity | ≦±2℃ | |||||||||||||||
| Size | Hanging blue size | External dimensions approx. | ||||||||||||||
| Volume(150L) | 60x50x50(WxHxD)CM | 165x185x160(WxHxD)CM(Motor height not included, detachable) | ||||||||||||||
| Power and net weight | 50L | 80L | 150L | |||||||||||||
| Model | D-40 | D-55 | D-65 | D-40 | D-55 | D-65 | D-40 | D-55 | D-65 | |||||||
| KW | 17.5 | 19.5 | 21.5 | 20 | 20.5 | 23.5 | 30 | 24.5 | 27.5 | |||||||
| KG | 850 | 900 | 950 | 900 | 950 | 1000 | 1050 | 1150 | 1250 | |||||||
| Voltage | (1)AC380V 50Hz Three-phase four-wire + protection ground | |||||||||||||||
Performance Indicators
Test environment conditions
The ambient temperature is +28℃. The relative humidity is ≤85%. There should be no specimen in the thermal shock chamber, unless specified otherwise.
Test standards met
- GB/T 2423.1-2001 Test A: Low temperature test method
- GB/T 2423.2-2001 Test B: High temperature test method
- GB/T 2423.22-2002 Test N:Temperature change test method Test Na
- GJB 150.3-1986 High-temperature test
- GJB 150.4-1986 Low-temperature test
- GJB 150.5-1986 Temperature shock test
- GB/T 5170.2-1996 Temperature test equipment
thermal shock testing machine Structural features
Insulation envelope
- Inside wall: SUS304 stainless steel plate thickness 2.0mm
- The welded SUS304 stainless steel plate makes up the base plate structure. No completed fusion welding.
- Built-in reinforcement, easy for users to test the bracket fixed
- Insulation material: rigid polyurethane foam + ultra-fine glass fiber
- Test chamber sample frame load-bearing capacity: 20kg / piece (uniform load)
- But the total load capacity of the box (bottom plate and sample rack together) does not exceed: 200kg
Test area door
Single door, hinge on the left (when facing the box) 1 set
Heater
- High-temperature chamber: Nickel-chromium alloy electric heater
- Low-temperature box: nickel-chromium alloy electric heating wire type heater
- Heater control mode: non-contact iso-periodic pulse width adjustment, SSR (solid state relay)
Circulation fan
- High-temperature exposure: centrifugal type 1 unit
- Low-temperature exposure: centrifugal type 1 unit
Drive Unit
Dampers drive and test area door locking device (pneumatic drive)
Air cylinder: low temperature / high temperature exposure 1
Main Body Structure
(1) High temperature zone
(2) Low temperature zone
Sealing device
Original imported high quality silicone sealing strip
Test door observation window (optional)
- The case requires a four-layer glass observation window
- The glass surface has an internal heater to prevent condensation and frost.
One hanging blue
Moving up and down by cylinder
Lighting (with window with)
A high-efficiency long-life Fei Li Po 5W lamp equips the box on the door.
Machine caster
It uses the multi-functional pulley movement to adjust the placement. It also ensures a strong bolt fixed position.
Alarm indicator
One alarm light
thermal shock test equipment Refrigeration system
Refrigerant
DuPont’s U.S. environmental protection is fluorine-free. It uses HFC R404A&R23, with an ozone depletion index of 0.
Condenser
Shell and tube type water-cooled heat exchanger

Evaporator
Stainless steel brazed plate heat exchanger

Throttle Device
Thermal expansion valve, capillary tube

Refrigeration Machine Control Mode
The control system automatically adjusts the operation of the refrigerator. This is done based on the test conditions.
With refrigerant servo valve flow rate algorithm control
Basic circuit
(1) Compressor return gas cooling circuit
(2) Energy regulation circuit
(3) Evaporative pressure regulating valve
(4) Servo-controlled snow circuit
(5) Water flow regulating valve
thermal shock test chamber Electrical control system
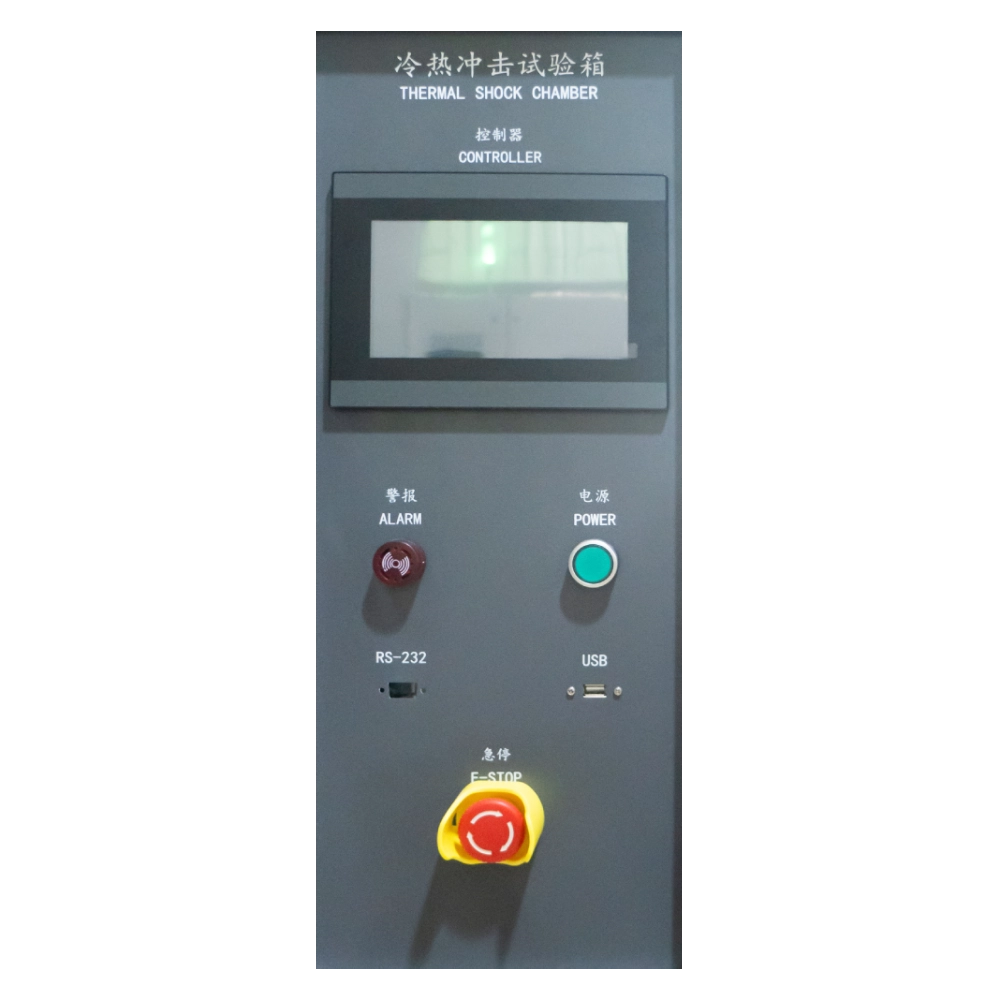
Controller
- Imported hardware, self-developed software
- Electromagnetic interference prevention (SGS, CE) certified controller
- Support language: Chinese (traditional, simplified) / English
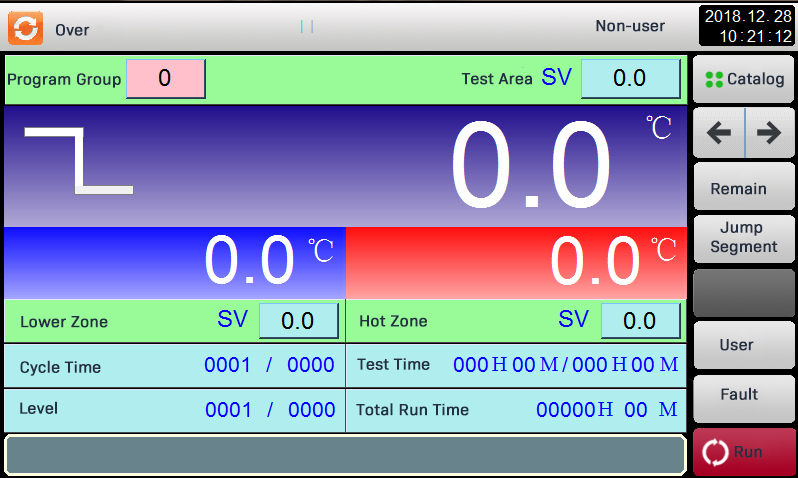
Display Systems
Temperature shock test chamber has a 10 inch LCD touch screen. The screen is high resolution and shows true color. It displays in English and Chinese. The resolution is 850*680.
- With USB download function, with RS232 interface, curve software, no recorder
- With vacuum glass observation window, more effective direct observation function
- Refrigerant servo valve flow algorithm control. Power saving 30%, there is a dormant function of the standing flow time, energy saving 50% or more.
- The controller has SGS certification. It is anti-electromagnetic interference. It has over 32 digital soft program matching. It has the first development and software upgrade function.
- Through the ISO-9001 quality certification (Taiwan & Dongguan & Suzhou)
- The defrost cycle occurs 1000 times. Each defrost happens once from -40 to 150 degrees. The goal is to ensure that each defrost completes within 2 hours. An integration test is conducted to achieve 25% energy savings.
Operation Mode
(1) Program mode
(2) Constant value mode
Programmable Touch Screen
High precision resistive touch screen
Input Mode
3 groups of inputs, support PT100, thermocouple T, K, E, etc.
Output Mode
PID+SSR/SCR automatic forward and reverse bi-directional synchronous output.
Accuracy
0.1 high precision sampling, temperature: 0.1℃
Built-in
(1) Super storage space, 24 hours of continuous power on can save 3 months of data
(2) Sampling for 1M, can replace the computer storage
Communication Function
The USB interface allows you to download historical curves and data. This can replace the recorder with RS485, LAN, or GPRS for communication. This enables convenient remote monitoring and data acquisition. USB function: USB 2.0, it records and download test operation data, with a flash drive (capacity of 4G)
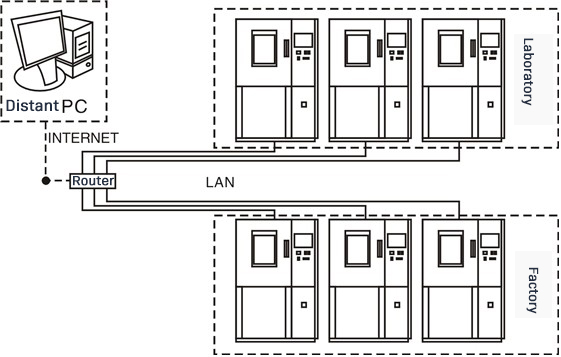
Local Area Network (LAN) connection for two computers and multiple controllers (optional)
WEB SERVER function can be realized our instrument communication customer factory (optional)
Defrost Setting
(1) Automatic setting times
(2) Manual setting times
(3) Defrost frequency meet: 1000 cycle/time (in the case of -40℃~150℃)
Fault Alarm Function
The prompts for faults in Chinese and English are humanized. They show the causes of faults and how to fix them. They can monitor 16 groups of fault alarms and outputs at the same time.
Setting Function
You can set automatic or manual energy storage compensation. You can also set pre-heat treatment before impact. You can set pre-cooling, time-keeping, and separate cold or hot flush.
Online Function
Provide strong communication environment and support 254 multi-branch structure.
Four Ways to End
(1) After a room temperature shock, stop.
(2) Stop after frost occurs.
(3) Stop directly when in the ready state.
(4) After power failure and restoration, select the “continue” or “re” stop setting.
Program Storage Capacity
(1) Thermal shock machine can have up to 127 programs that run for a long time.
(2) Each segment can run for a maximum of 999 hours, with a maximum of 32000 cycles.
(3) This can repeat each command up to 9999 times, within a time range of 0 to 99 hours and 59 minutes.
(4) During program execution, a real-time graphical curve can be displayed. This curve shows the temperature setting (SV) and the actual temperature (PV). It also shows the program cycle and curve function. It shows segment time and segment number time. It also shows operation time, fault state, and fault time. Additionally, there is a file skip and hold function available during program execution.
Intelligent Screen Saver Function
- Thermal shock test chamber can use the screen protector to protect the screen.
- Thermal shock environment chambercan adjust the screen protection duration.
- Temperature shock chambercan set the machine’s operation password authority.
Circuit Control
thermal shock test chamber Safety protection device
Refrigeration System
(1) Compressor overpressure protection
(2) Compressor electrical overheating
(3) Compressor motor overcurrent
Electrical System
- Thermal shock testing machinecan adjust the over-temperature protection for safety.
- The test space has a temperature fuse for protection.
- The air conditioning channel can experience overtemperature, which needs protection.
- There is a protector for leakage and short circuit situations.
- The total power has phase sequence protection.
- Overload circuit break protection is in place for safety.
- Load short circuit is protected against as well.
thermal shock chamber Standard distribution
(1) The power cable consists of five lines, including a four-core cable and a protection ground wire. The cable is approximately 2.5 meters long.
(2) Select a hole with a size of 50 / 100MM for testing purposes.
(3) Place the products with two layers of laminate.
(4) These need one copy of the product manual.
(5) Additionally, one copy of the factory test report is necessary.
thermal shock chamber Packaging and transportation
The thermal shock test chamber is essential and transported as a whole. The outer box size parameter determines the maximum transport size. The box size determines the maximum transport size, excluding packaging.
Conditions of use
Installation Site
(1) The installation site has a smooth ground.
(2) There is good ventilation and no strong vibration around the equipment.
(3) There is no strong electromagnetic field around the equipment.
(4) There are no flammable, explosive, corrosive substances, or dust around the equipment.
(5) The equipment is equipped with nearby drainage floor drains.
(6) The ground bearing capacity of the site must be at least 800kg/m2. There must be at least 600mm of space around the test chamber. Additionally, there should be a minimum of 800mm of space above for use and maintenance.
Environmental conditions
(1) Temperature: 5℃~35℃
(2) Relative humidity: ≤85%
Air source (compressed air)
(1) Air pressure: 86kPa~106kPa
(2) Air source (compressed air) pressure: (4~7) kg/cm2
Connection pipe diameter: φ8mm
Cooling Water Supply Requirements
(1) The frequency is set at 50±0.5Hz.
(2) The circulating water flow is approximately 16~20 T/h.
(3) The cooling water tower and water pipe have a water flow of 15 square / hour and a water pipe size diameter of 1.5 inch.
Power Supply Conditions Power Supply
(1) The power supply is AC380V 50Hz three-phase four-wire with protection ground.
(2) The voltage fluctuation range allowed is AC (380±38) V.
(3) The frequency fluctuation range allowed is (50±0.5) Hz.
(4) The resistance of the protective earth ground must be less than 4Ω.
(5) To use TN-S or TT mode power supply, install a capacity air or power switch at the site. This switch must be independent for the equipment’s use.
thermal shock test chamber Main accessories list
Water-cooled chiller diagram (optional)
FAQ About Two Zone Thermal Shock Tester
The thermal shock tester serves different purposes for each stage of product development.
- During product development, it identifies issues in design and processes.
- Product finalization or design identification and batch production stage acceptance decision-making to provide a basis;
- In order to troubleshoot early product failures, environmental stress screening is applied.
- Reliability: The cold and hot shock test chamber can simulate extreme environmental conditions and conduct all-round testing of products, thus ensuring their reliability and weather resistance.
- High efficiency: The thermal shock chamber can test multiple samples at the same time, greatly improving the testing efficiency.
- Repeatability: The cold and thermal shock test chamber can be set up through the programme to carry out repetitive tests to ensure the consistency of product performance.
- Flexibility: The cold and thermal shock test chamber can be customised and modified according to different testing needs to meet a variety of different testing requirements.
- Energy-saving and environmental protection: The cold and thermal shock test chamber adopts advanced energy-saving technology, which can minimise energy consumption, while using environmentally friendly refrigerants to reduce the impact on the environment.
Cold and thermal shock testing simulates the use of a product under extreme temperature conditions and assesses the reliability and durability of the product. Through this test, performance problems that may occur during temperature changes can be identified and solved, improving the quality and reliability of the product.
The test duration and temperature range should be determined based on product design requirements, industry standards and customer needs. The test time can vary from a few hours to a few days. The temperature range is determined by the extreme temperatures.
- Electronic Product Testing:
The cold and thermal shock test chamber is used for electronic product testing. This design verifies the reliability and durability of electronic products, hardware, and circuitry. The test chamber subjects the products to different temperature change conditions. Ensuring electronic products work in harsh environments is essential. - Automotive Vehicle and Parts Testing:
Thermal shock test chamber can test the engine, transmission, battery and other automotive parts. Tests are done to ensure the car functions in extreme conditions. The reliability of a vehicle can be assessed with complete trials. - Product Performance Evaluation:
Thermal shock chamber can evaluate product performance, such as breaking strength, coefficient of thermal expansion, durability, and other properties, which are useful to ensure that a product will not break or be damaged in extreme environments, which is important for improving product design and selection. - Testing of Optoelectronic Devices:
Tests of optoelectronic devices are conducted for performance and power in extreme temperatures. These devices include LED lamps and solar panels. Thermal shock test chambers test them. This is very important for the application and development of optoelectronic devices.
- Avoid turning the refrigeration unit on and off within three minutes. This can affect the function of the compressor.
- The tester cannot test or heat flammable, explosive and corrosive substances. Failure to do so will result in accidents or damage to the machine.
- One should not place samples in the test chamber. Excessive samples will disrupt air circulation in the chamber, affecting its performance.
- When someone use the door, they should close it. Otherwise, temperature leakage may affect the performance of the region.
- Designated personnel to operate the machine, so as not to cause early damage to the machine.
- Icing occurs on the interior evaporator and sealed areas. This happens when someone opens the door during the test. As the temperature gets lower, the icing will get worse. If someone needs to open the door, please open and close it as soon as possible.
- Wait for the machine to stop after completing the operation. Then, open the door to retrieve the test product.
- Do not open the door during operation unless necessary. Opening it may lead to adverse consequences. High temperature gas rushing out of the chamber …………… is very dangerous!
The inside of the door remains at a high or low temperature ……… causes accidents!
Excessive temperatures may trigger the fire alarm and cause false action! To avoid injury, open the door to prevent hot air. When the operator opens the door, he must move backward in the direction of the opening. - Ground the test chamber to avoid electrostatic induction.
- The circuit breaker is a safety device that protects against overheating. The design aims to safeguard both the machine and the operator. Please remember to check it.
- Please do not touch the inspection during operation to avoid electric shock or injury to the fan. Stop the operation first and turn off the power before repair to prevent danger.
- Non-functional personnel cannot perform machine maintenance and inspection. Full-time staff members do these tasks. A guardian must be present to prevent unauthorized power on and off. This can cause electrocution injuries.
The thermal shock test is also called the temperature shock test. It subjects a test specimen to low and high-temperature air (or a suitable inert gas) and rapid temperature changes. So, it can test the ability of components, equipment, and other products to handle rapid temperature changes. This assesses how well products handle rapid temperature changes. It is essential for the identification and batch production stages of routine tests.
In some cases, it is used for stress screening tests. The use of cold and thermal shock test chambers is second only to vibration and high and low-temperature tests. They are key for checking and improving equipment’s ability to handle its environment.
In fact, the cold thermal shock test chamber is a tool. It is used at different stages of product development for different purposes.
- The development stage can find design and process defects.
- This provides a basis for deciding if a product is ready for batch production.
- These tests are for environmental stress screening. They aim to find the product’s early failures.
Hot and cold shocks can cause thermal and cooling stresses to be generated in materials. The following are the specific reasons why both stresses are generated:
1. Generation of thermal stresses
When a material undergoes a sharp change from a high to a low temperature, the temperature of different parts changes at different rates, thus creating a temperature gradient, i.e. a temperature difference. Different parts of the material also have different coefficients of thermal expansion. As a result, an uneven strain occurs within the material, which leads to the generation of internal stresses.
2. Generation of cooling stresses
At the end of the impact, the material undergoes a cooling process from high temperature to room temperature. However, the cooling rate varies at different locations of the material, and the fast-cooling part produces different stresses from the slow-cooling part, resulting in an uneven strain in the material.
From the above analyses, it is known that thermal and cold shocks can cause huge stresses on the material, which can lead to irreversible damages such as cracks and breaks. Moreover, different materials have different ability to withstand hot and cold shocks, and some brittle materials (e.g. glass) are easily destroyed under the action of thermal stress and cooling stress.
In order to avoid the damage caused by hot and cold shock to the material, we can take the following measures:
- Slow heating up and cooling down: Slow heating up or cooling down methods can be used to slow down the generation of temperature gradients, thus reducing the effects of thermal and cooling stresses. For example, the material can be heated in an oven or cooled down at a slow rate.
- Use of materials resistant to thermal stress and cooling stress: some materials have relatively strong resistance to thermal stress and cooling stress, such as its coefficient of thermal expansion and temperature changes in relation to the relatively flat. The use of these materials can reduce the internal stresses caused by temperature changes.
- Reduce sudden temperature changes: materials are greatly harmed by sudden temperature changes, so we can use progressive heating or cooling to reduce the degree of sudden temperature changes.
In short, thermal shock will bring irreversible damage to the material, so we need to take appropriate measures to avoid this damage.
- Mechanical properties: Cold and thermal shock testing may result in changes in the mechanical properties of the material, such as tensile strength, bending strength, impact strength, etc. This is because the material is subjected to different temperatures. This is due to the thermal expansion and contraction of the material at different temperatures, leading to changes in the stress distribution within the material.
- Dimensional stability: Cold and thermal shock tests may result in changes in the dimensional stability of the material, such as dimensional expansion, contraction or deformation. This is due to the thermal expansion and contraction of the material at different temperatures, resulting in changes in the dimensions of the material.
- Chemical properties: Cold and thermal shock tests may result in changes in the chemical properties of the material, such as corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, oxidation resistance, etc. This is because the material undergoes thermal expansion and contraction at different temperatures, resulting in changes in the material’s dimensions. This is due to the fact that chemical reactions occur in materials at different temperatures, leading to changes in the chemical properties of the material.
- Microstructure: Cold and thermal shock tests may lead to changes in the microstructure of the material, such as grain size, phase transition, dislocation density, etc. This is because materials undergo microstructural changes such as phase transitions or dislocation shifts at different temperatures.
First, the cooling process: these two test chamber are to industry to do high and low temperature test. But they have a fundamental difference is that the high and low temperature test chamber is to see the industry in the cooling process to sense the transformation of the industry and the cold thermal shock test chamber does not have this cooling process, it is to make the industry instantly sense the temperature change and change.
Second, the scope of application: high and low temperature test chamber for electrical and electronic industries, components, parts and their materials in the high and low temperature environment, storage, transport and use of adaptability tests, as well as temperature gradient test. Carbon dioxide incubator controller circuit consists of temperature sensor, voltage comparator and control execution circuit. It can also carry out stress screening test for electronic components.
Cold and thermal shock test chamber is mainly for electrical and electronic industry machine and components for cold test, rapid temperature change or gradual change in the conditions of adaptability test chamber, especially for electrical and electronic industry environmental stress screening (ESS) test. Biochemical incubator with refrigeration and heating two-way thermoregulation system, temperature-controllable function, is biology, genetic engineering, medicine, health and epidemic prevention, environmental protection, agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry and other industries, scientific research institutions, colleges and universities, production units or departments of the laboratory of the important experimental equipment, widely used in low-temperature and constant-temperature test, culture test, environmental testing, and so on. Carbon dioxide cultivation is a device to cultivate cells/tissues in vitro by simulating the formation of a growth environment similar to that of cells/tissues in a living organism within the incubator box, which requires a stable temperature (37°C), a stable level of CO2 (5%), a constant acidity and alkalinity (pH: 7.2-7.4), and a high relative saturated humidity (95%). The test equipment is mainly used for the industry in accordance with the requirements of the G standard (approval issued by the G standardisation authority) or the user’s own requirements, in the high temperature and low temperature instantaneous change conditions, the industry’s physical and other relevant characteristics of the environmental simulation test, after the test, through the test (check and test), to determine the performance of the industry, whether it can still meet the predetermined requirements for industrial design, improvement, Identification and factory inspection.
Third, the temperature conversion speed: temperature cycling test chamber relative conversion speed to be slow, due to the diversity of test demand, manufacturers will manufacture a variety of non-standard industries in accordance with the requirements of the guests, different configurations require speed is not the same, before you buy, please explain the situation with the manufacturer and the requirements, or to do a more economical conventional machine temperature rise and fall speed of 1 to 3 degrees / minute or so conventional high and low temperature box, that is, the temperature rises 3 degrees Per minute, cooling one degree per minute of cold and thermal shock test chamber temperature conversion speed is very fast, generally from high temperature to low temperature conversion time within 3 to 5 minutes can be completed, also known as high and low temperature shock test chamber or rapid temperature temperature change test chamber. While the conventional thermal shock test chamber, it is within 5 minutes to quickly complete the high temperature to room temperature or room temperature to low-temperature conversion, the essential difference is that the temperature change time spent is not the same.
Fourth, humidity: cold thermal shock test chamber without humidity, temperature cycling test chamber can choose to do humidity test.
- So that the electronic product insulation or sealing with slurry melting loss, grease melting loss, thus causing damage. Accelerate the deterioration and aging process of polymer materials and insulation materials, shortening the service life of the product.
- High temperature will make the shape of plastic materials change, the temperature is too low will make the electrolyte solidification, resulting in electrolytic capacitors, batteries can not be used normally.
- The viscosity of the lubricant increases, and even condensation and ice, affecting the starting performance of the product, affecting the normal starting of electronic products, increasing the instrument error.
- So that the material becomes brittle, such as plastic, steel, etc., easy to brittle crack damage at low temperatures, rubber material hardness increases, elasticity decreases.























