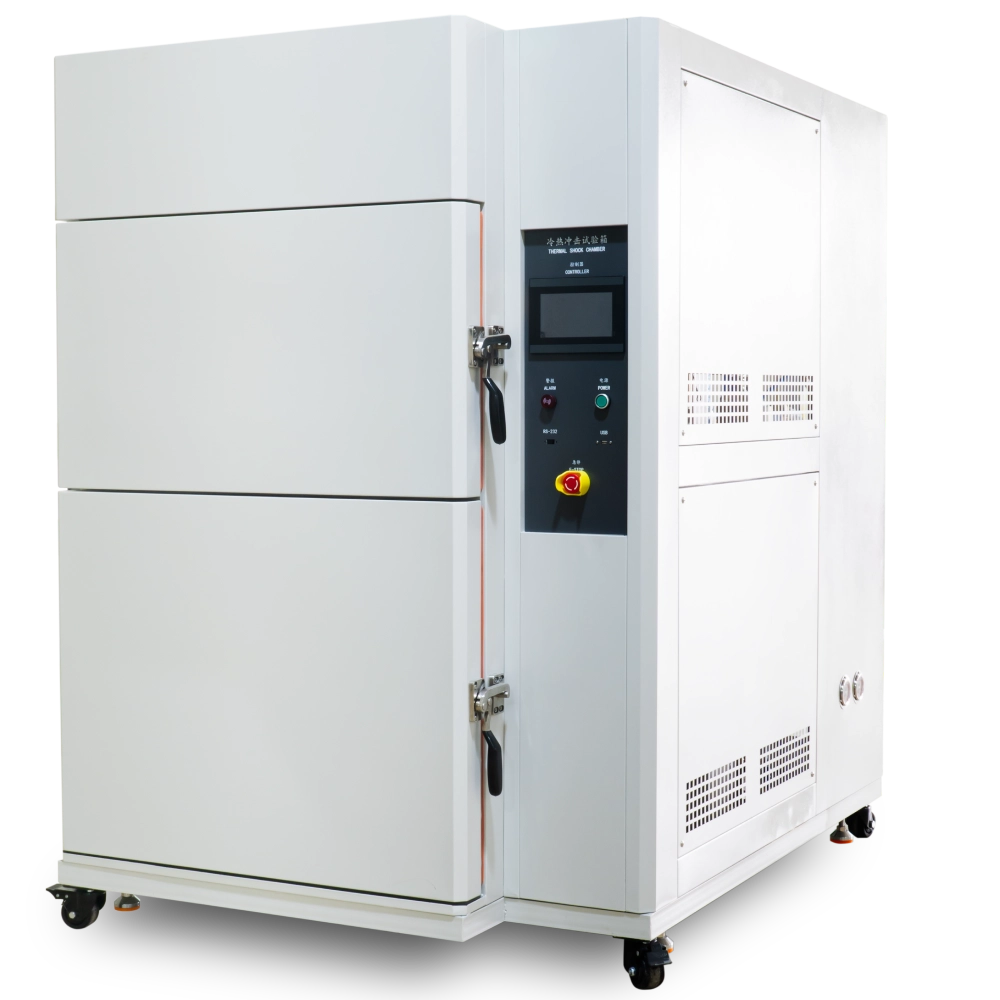
Manufacturers use a Thermal Shock Test Chamber to test how materials react to extreme temperature changes. A thermal shock test chamber switches between hot and cold temperatures. This simulates the actual conditions a product might experience.
These chambers are important in many industries. Some include:
- Electronics: These chambers test electronics like phones and laptops to check how they handle different climates.
- Automotive: Thermal shock chambers test car parts like engine parts and paint finishes.
- Aerospace: These chambers test aerospace parts to see how they handle extreme temperature changes.
- Pharmaceuticals: Thermal Shock Chambers help ensure drugs stay stable at different temperatures.
Thermal shock chambers help products last longer and perform better, making customers happy. They play a key role in making sure everyday items, like cars and medicine, are high-quality and long-lasting.
How Does a Thermal Shock Chamber Work?
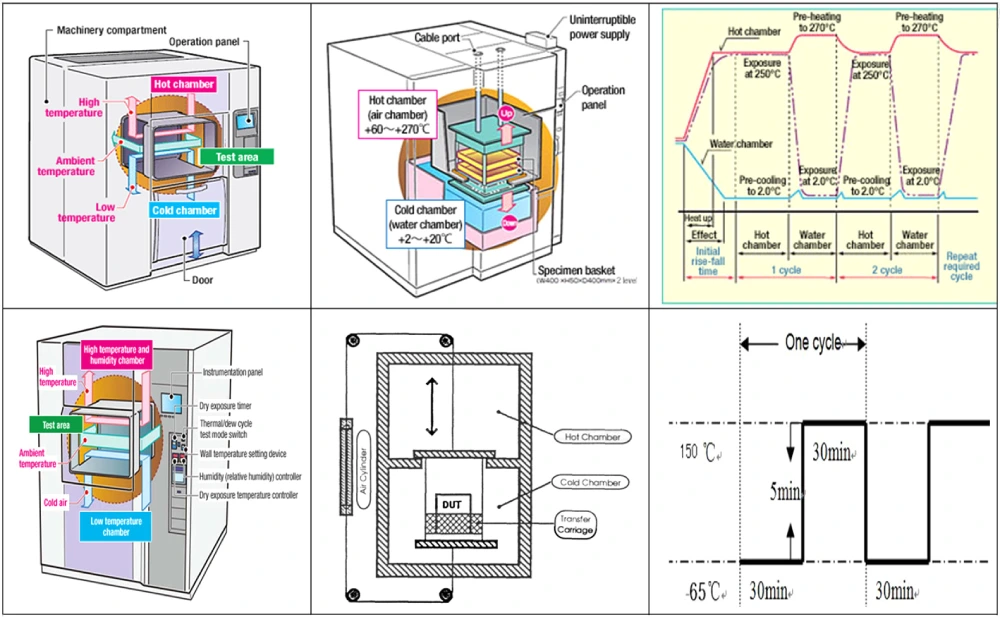
A thermal shock chamber has several steps in its process. Here’s what happens:
- Test Preparation: The operator puts the product or material in the chamber, placing it right for accurate results.
- Setting the Temperatures: The operator sets the chamber to specific hot and cold temperatures based on what conditions the product might face.
- High Temperature Exposure: The chamber raises its temperature to the set high point. The product stays in this hot environment for a set time.
- Rapid Temperature Change: After the high temperature, the product is quickly moved to the cold zone. This quick change creates thermal shock.
- Low Temperature Exposure: In the cold zone, the product is exposed to the low temperature for a set time.
- Return to High Temperature: The product goes back to the high-temperature zone, finishing one cycle of testing.
- Repeat Cycles: The technician repeat Steps 3 to 6 as needed based on the test requirements.
This process shows how products handle quick temperature changes. This information helps manufacturers improve their designs. It also helps find any weak points in products to fix before they reach customers. Thermal shock chambers are essential for ensuring products are high-quality and durable.
What’s a Two-Zone Thermal Shock Chamber?
A two-zone thermal shock chamber has two separate zones for high and low-temperature testing. This design helps switch between the two temperature extremes, making the testing process easy.
In two-zone chambers, the test sample is moved between a low-temperature chamber and a high-temperature chamber. This design is fast and simple. However, moving the test samples might put extra stress on them, which could affect the test results.
Many industries find applications for two-zone thermal shock test chambers. Some examples include:
- Electronics: Testing parts like circuit boards and semiconductors.
- Automotive: To test various car parts like engine components to make sure they can handle different temperatures.
- Aerospace: Two-zone chambers test parts like turbine blades and space vehicle components.
- Materials Science: They use these chambers to study the effects of temperature changes on different materials.
Two-zone thermal shock chambers are useful for simulating quick temperature changes, making them valuable in many industries.
What’s a Three-Zone Thermal Shock Chamber?
A three-zone thermal shock chamber has an extra zone for room-temperature testing. Manufacturers use this third zone as a rest area for the test sample during testing cycles.
The test sample in a three-zone chamber stays in place, unlike in two-zone chambers. The testing area moves hot and cold air around the sample to create thermal shock. This feature helps avoid extra stress on the sample from moving it, giving more accurate results.
However, three-zone chambers are more complex and may cost more than two-zone chambers.
Three-zone thermal shock chambers are used in many industries. Some include:
- Electronics: Three-zone chambers often test complex devices like microprocessors and integrated circuits.
- Aerospace: Critical components such as satellite parts and propulsion systems undergo testing in these chambers to simulate space conditions.
- Automotive: Parts like battery systems and brake components are tested for thermal shock resistance.
- Military: The defense industry uses these chambers for rigorous testing of weapons systems and other equipment.
Three-zone thermal shock chambers offer more detailed testing and are an important tool in many industries. Even though they cost more and are more complex, they are an excellent investment.
Two-Zone vs. Three-Zone Thermal Shock Chambers: Which is Better?
There are differences between the two-zone and three-zone thermal shock chambers. Here’s what they are:
- Zone Count: Two-zone chambers have a hot and cold zone. Three-zone chambers have an extra room-temperature zone.
- Test Sample Movement: In two-zone chambers, the test sample is moved between the hot and cold zones. In three-zone chambers, the sample stays in place, and the surrounding air is moved.
- Complexity and Cost: Two-zone chambers are simple and may cost less. Three-zone chambers are more complex and may cost more.
- Industry Applications: Both types of chambers are used in many industries. Two-zone chambers test products like circuit boards, engine components, and turbine blades. Three-zone chambers test complex systems like microprocessors, battery systems, satellite parts, and military equipment.
The choice between two-zone and three-zone chambers depends on the needs of the product, budget, and test complexity.
What’s the Future of Thermal Shock Chambers?
Both two-zone and three-zone thermal shock chambers are essential in many industries. While two-zone chambers are fast and simple, three-zone chambers are more accurate. The choice depends on the product’s testing needs, budget, and the complexity of the test.
In the future, there may be more advances in thermal shock testing. This could include chambers with more zones, finer temperature controls, or the ability to simulate other environmental factors. As we move forward, the demand for reliable products will continue to drive innovation in this field.
Standards for Thermal Shock Test Chamber
There are different standards for thermal shock chambers and their testing procedures. These standards guide how tests should be done and results interpreted. Some include:
- IEC 60068-2-14
- MIL-STD-202G, Method 107G
- MIL-STD-810G, Method 503.5
- JESD22-A104E
- ISO 16750-4
- RTCA DO-160, Section 5
- ISTA 2A
- BS EN 1367
- ASTM C1525
- BS EN ISO 13807:2022
- BS EN 1183
The right standard to follow depends on the application and industry. It’s important to consult with a testing professional or industry expert to make sure you’re following the right procedures.
For more environmental test chamber, Please visit: https://chiuventionclimatechamber.com
For more environmental test simulation programmes,environmental testing knowledge, instrument knowledge, and environmental testing laboratory knowledge, please contact us: [email protected]

